HIPEC surgery (Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy) is a two-step procedure that treats certain cancers in the abdomen.
If cancer develops in one organ in the body and is left untreated, it first spreads to the surrounding organs and then to other organs in the body through the blood. In the case of cancers of the digestive system in particular, metastasis usually occurs to the lungs, liver and peritoneum, i.e. the lining of the abdomen. You can read about how cancer cells find their way here.
Until a long time ago, patients with advanced peritoneal cancer received only chemotherapy and thus lived only 6 months longer than a patient in the same situation who did not receive chemotherapy. However, with the development of “Cytoreductive Surgery” and “Hypertermic Chemotherapy” methods, patients can be kept alive for up to 11 years.
What is HIPEC – Cytoreductive Surgery?
Today, surgical methods applied for advanced ovarian, colon, peritoneal and gastric cancers are not only based on tumour excision, but also include more complex procedures. Cytoreductive surgery is the surgical removal of all macroscopic peritoneal findings. Cytoreductive surgery includes visceral or parietal peritonectomy. The aim here is to resect all macroscopic tumour formations and eliminate pathological risks. In cytoreductive surgery, the surgeon uses an electrosurgical tool, the “Handpiece”. The handpiece generates heat through high-voltage electricity and burns the cancer tissue with the generated heat.
What is Hypertermic Chemotherapy?
Hypertermic Chemotherapy, also known as Hyperthermic Intra Peritoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC), is the application of heated chemotherapy solution to the abdominal cavity to destroy microscopic tumours after removal of macroscopic tumours with “Cytoreductive Surgery” in patients with cancer spread in the abdominal region. Immediately after tumour resection, heated chemotherapy solution is applied to the patient’s abdomen to eliminate microscopic malignancies.
Hypertermic chemotherapy is most commonly used to treat colorectal cancers and appendicitis tumours. It is also used for:
- Adrenal Cancers
- Ovarian Cancer
- Liver Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Mesothelioma
It is also used to treat cancers such as cancer. The fact that a person has one of the above diseases does not always mean that the person will be treated with Hypertermic chemotherapy. In order to determine whether the patient is suitable for Hypertermic chemotherapy, factors such as the patient’s general health condition, age, type of cancer, etc. should be taken into consideration. If the answer to one or more of the following questions is “Yes” for the patient, Hypertermic chemotherapy will not be beneficial.
- Has the cancer tissue spread into the abdominal cavity?
- Is the patient older than 75 years?
- Has the patient previously undergone a heavy chemotherapy process?
- Does the patient have liver or kidney failure?
How is the Hypertermic Chemotherapy Method Applied?
Stage 1: Surgical Intervention
First of all, the doctors excise as much tumour as they can from the abdominal cavity by means of “cytoreductive surgery”. Cytoreductive surgery must be performed before Hypertermic chemotherapy. Otherwise, Hypertermic chemotherapy cannot reach deep into the cancer tissues and the treatment cannot be effective enough. However, some patient circumstances may make it impossible for the patient to undergo surgery. In such a case, doctors have to take another course of treatment.
Phase 2: Hypertermic Chemotherapy Bath
Immediately after the surgery, Hypertermic chemotherapy, which is heated during the operation and administered once, is used to destroy invisible cancer tissue.
Carboplatin, cisplatin, doxorubicin, gemcitabine and pemetrexed are also used in Hypertermic chemotherapy. However, this time the drugs are not injected into the bloodstream, but are instead given directly into the abdominal cavity.
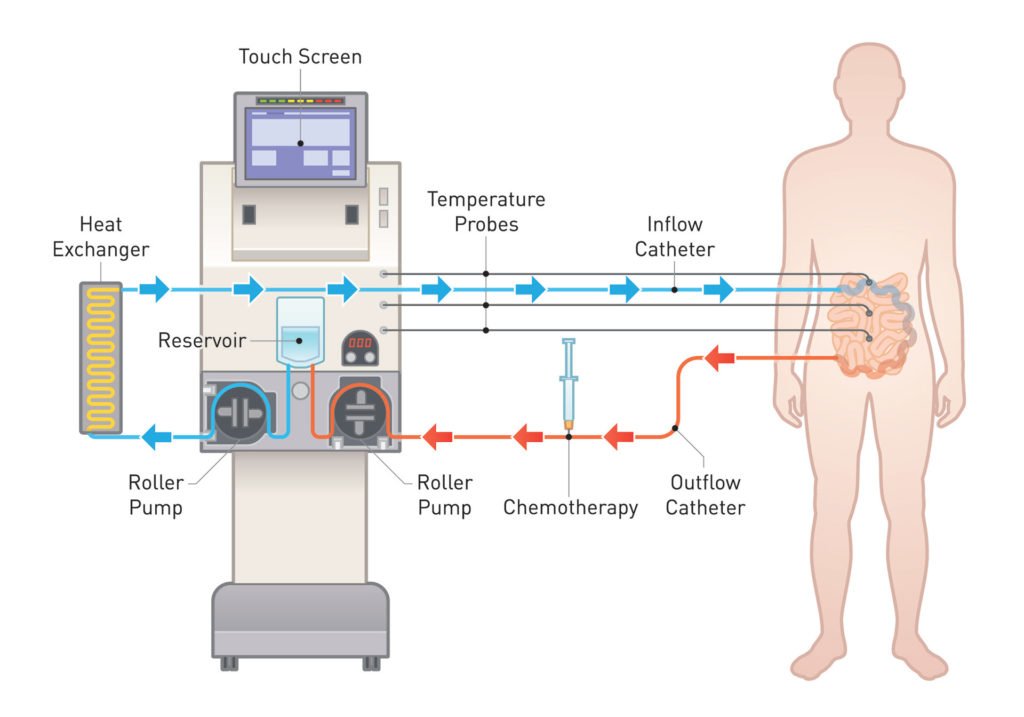
How Does Hypertermic Chemotherapy Machine Work?
The mechanism can be summarised as follows:
After inserting the catheter into the abdominal cavity, the doctor connects the catheter to the “Perfusion System”, which heats the chemotherapy solution and sends it into the body and at the same time withdraws the solution from the body.
As the chemotherapy solution passes through the heating unit of the perfusion system, its temperature rises to 42-43 degrees. At this temperature, cancer cells are damaged while normal cells are not.
The doctor massages the abdomen by hand to mix the solution well. Thus, the Hypertermic chemotherapy solution reaches the cancer cells more easily.
This process takes about 1-1.5 hours.
After the chemotherapy is finished, the doctor ensures that the chemotherapy solution is drained from the body.
Finally, the cavity is rinsed with saline solution before the catheter is removed and the incision is closed.
This whole process takes between 6 and 18 hours. The more tissues in the body the cancer has spread to, the longer the procedure takes.
Why are chemotherapy drugs given by heating?
The main reason why chemotherapy drugs are given by heating is that heat itself has an anti-tumour effect. However, heat ensures that the drug is evenly distributed on the surfaces in the abdomen.
It is a known fact that heat facilitates the penetration of anti-cancer drugs into the tissue and thus increases the effect of chemotherapeutic agents to kill cancer cells.
Recovery Process
The healing process after Cytoreductive Surgery and Hypertermic Chemotherapy continues for months. The lengthening or shortening of this process also depends on the lifestyle adopted by the patient during the healing process. The most difficult situation for the patient during the recovery process is the feeling of fatigue. The feeling of fatigue ends 2-3 months after the operation. It is also very important to lead an active life within reasonable limits and to eat well during the healing process.
Side Effects and Risks of Hypertermic Chemotherapy
Although the side effects of Hypertermic chemotherapy are similar to those of regular chemotherapy, the severity of the side effects is much milder than with regular chemotherapy.
Side effects
Nausea and vomiting: If necessary, this side effect is prevented by giving anti-nausea medication to the patient.
Lethargy/Fatigue: It is considered normal to feel tired after a long operation. It takes three months for the patient to return to normal and for the feeling of fatigue to disappear.
Decrease in appetite
Diarrhoea: one of the most common side effects patients experience. Diarrhoea is not caused by chemotherapy, but by the procedure itself.
In rare cases, intense hair loss may occur after Hypertermic chemotherapy.
Sores in and around the mouth
Risks
After Hypertermic chemotherapy, patients may develop inflammation of the lungs.
Pancreatitis occurs in 7 out of every 100 patients treated with Hypertermic chemotherapy.
Bleeding and intestinal leakage develop in 4 out of every 100 patients.
Since the number of White Cells in the blood decreases after Hypertermic chemotherapy, the risk of infection increases.
Substances in the intestine can leak into the abdomen and cause intra-abdominal infections.

Is Hypertermic Chemotherapy an Experimental Treatment?
Hypertermic chemotherapy is a treatment method that has been proven successful by research. No organisation uses Hypertermic chemotherapy for experimental purposes.
What are the differences between Hypertermic chemotherapy and normal chemotherapy?
In normal chemotherapy, the drug is given directly into the blood, while in Hypertermic chemotherapy, the drug is given into the abdominal cavity. With Hypertermic chemotherapy, it is easier to kill cancer cells in the abdominal cavity that are difficult to kill.
Hypertermic chemotherapy is a treatment method that makes it possible to administer high doses of chemotherapy, concentrating the chemotherapy in the intraperitoneal region and minimising the exposure of the rest of the body to chemotherapy. However, the side effects of Hypertermic chemotherapy are lower and Hypertermic chemotherapy enhances the effect of chemotherapy on cancer cells by increasing chemotherapy absorption.
Factors Affecting the Success of Hypertermic Chemotherapy Treatment
Factors such as the extent to which the disease has spread throughout the body, the timing and size of the surgical intervention, the diameter of the tumoural masses, the histology of the tumours, the sensitivity of the tumour to chemotherapy, the sensitivity of the tumour to chemotherapeutic drugs and the duration of chemotherapy affect the success of the treatment.
Treatment after Hypertermic chemotherapy
There are multiple factors that affect the prognosis after Hypertermic chemotherapy, such as the severity of the disease at the time of diagnosis, how much of the tumours were excised by surgical intervention and the patient’s condition. Although a new chemotherapy period does not usually start for patients after Hypertermic chemotherapy, in some cases chemotherapy may be administered for 4-6 weeks. Chemotherapy may not be suitable for every Hypertermic chemotherapy patient. Because the conditions of the patient may not be suitable for this.
Cost of Hypertermic Chemotherapy
It is not possible to say an exact price for Hypertermic chemotherapy. Because cancer is an individualised disease and accordingly, the treatments applied to patients vary from person to person. While calculating the cost, factors such as how many days the patient will stay in the hospital, which team will operate on the patient, operating theatre and chemotherapy drugs are taken into consideration.
Success Rate of Hypertermic Chemotherapy
Until the 2000s, only chemotherapy was applied to end-stage patients with intra-abdominal cancers and the patient was kept alive for a maximum of 6 months. However, with the Hypertermic chemotherapy method, patients can live for a period ranging from 5 to 11 years.
While the 5-year survival rate in peritoneal cancers is between 66-97 per cent, this rate is around 50 per cent in ovarian cancer. This rate is even lower in colorectal cancers.
The mortality rate after Hypertermic chemotherapy is between 0% and 7%. This rate is considered low for Hypertermic chemotherapy applied for end-stage cancer patients.
Does Hypertermic Chemotherapy Have No Effect on Colorectal Cancer?
In an article published in April 2018, it was emphasised how effective Hypertermic chemotherapy is in the combined application of Hypertermic chemotherapy and cytoreductive surgery for advanced colorectal cancer patients for about 15 years. This study is the first study to evaluate the effects of Hypertermic chemotherapy on colorectal cancer. 265 patients with end-stage colorectal cancer without metastasis to any part of the body were studied in this study. These 265 patients either received oxiplatin heated to 43 degrees centigrade in the abdomen immediately after cytoreductive surgery or underwent surgery alone.
The median survival in the HIPEC group was 41.7 months, while the median survival in the surgery-only group was 41.2 months.
The mortality rates of both groups were equal and the side effects were similar in both groups.
According to ASCO Expert Andrew Epstein, this study has an important role in protecting most patients with colorectal cancer from unnecessary chemotherapy.
References:
1-K. Selby. Hipec Treatment For Mesothelioma Patients. Asbestos.com
2-Rogel Cancer Center. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy. Rogel Cancer Center
3-Hipec. The Hipec-Treatment. Hipec
4-UCI Health. Hyperthermic Intraoperative Peritoneal Chemotherapy. UCI Health